AFIB INFORMATION
AFIB INFORMATION
AFIB INFORMATION
AFIB INFORMATION
(Also called: AF, a-fib)
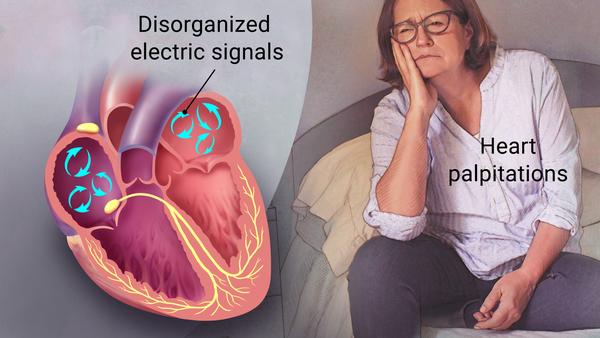 Atrial fibrillation is a quivering or irregular, often rapid heartbeat (arrhythmia) that commonly causes poor blood flow. The heart's upper chambers (atria) beat out of coordination with the lower chambers (ventricles). Afib can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. At least 2.7 million Americans are living with AFib.
Atrial fibrillation is a quivering or irregular, often rapid heartbeat (arrhythmia) that commonly causes poor blood flow. The heart's upper chambers (atria) beat out of coordination with the lower chambers (ventricles). Afib can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. At least 2.7 million Americans are living with AFib.This heart condition requires a medical diagnosis and may have no symptoms; but when symptoms do appear they include palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
People may experience:
The most common method of diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation is an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Even though an irregular pulse or feeling of heart palpitations can suggest atrial fibrillation, the electrical activity of the heart captured by an ECG is the best way to diagnose the AFib.
Treatment consists of blood thinners and beta blockers and can include: